An investor can buy and hold cryptocurrencies hoping they grow in value or trade their assets. What if you don’t want to do either? What if you could hold your digital assets and start making a profit at the same time? One way to make passive income with crypto that way is staking. What is staking crypto? How does it work, and what are its pros and cons? Like with any other passive income method, it is important to learn the answers to these questions.
Staking Crypto is Growing in Popularity
As the popularity of earning tokens by mining proof-of-work (POW) blockchains has waned, with Bitcoin a market exception, crypto-enthusiasts have consistently turned their attention to the staking game.
All told, the assets of staked crypto held by major exchanges like Binance totaled over 20 billion EUR as of January 2021, with Kraken’s platform alone holding over a billion euros worth of staked crypto.
WHAT IS STAKING CRYPTO?
Staking is the process of actively participating in transaction validation (similar to mining) on a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain. Anyone with a minimum-required balance of a specific cryptocurrency can join a staking pool, validate transactions, and earn staking rewards on these blockchains.
When you stake cryptocurrency, you are participating in the validation of transactions. This is a similar process to the mining we see on proof-of-work (PoW) blockchains (without the mining hardware!) Staking is a new type of consensus mechanism on the PoS blockchain. A user can stake their money on such a network to validate nodes or transactions. When users do this, they receive rewards.
A user can stake funds by locking or holding them in a cryptocurrency wallet. Locking or holding should usually last for a defined period of time. The wallet should allow the proof-of-stake mining operation to function. In a proof-of-stake blockchain, mining is replaced by the staking of funds to help achieve consensus across the network.
When staking, the number of coins “locked” inside a user’s wallet determines their right to validate transactions. Just like with mining, the goal is to add new transactions and blocks to the blockchain. In addition to the incentives for stakers, the scalability and high transaction speeds of PoS blockchains serve as other major benefits.
HOW DOES STAKING WORK?
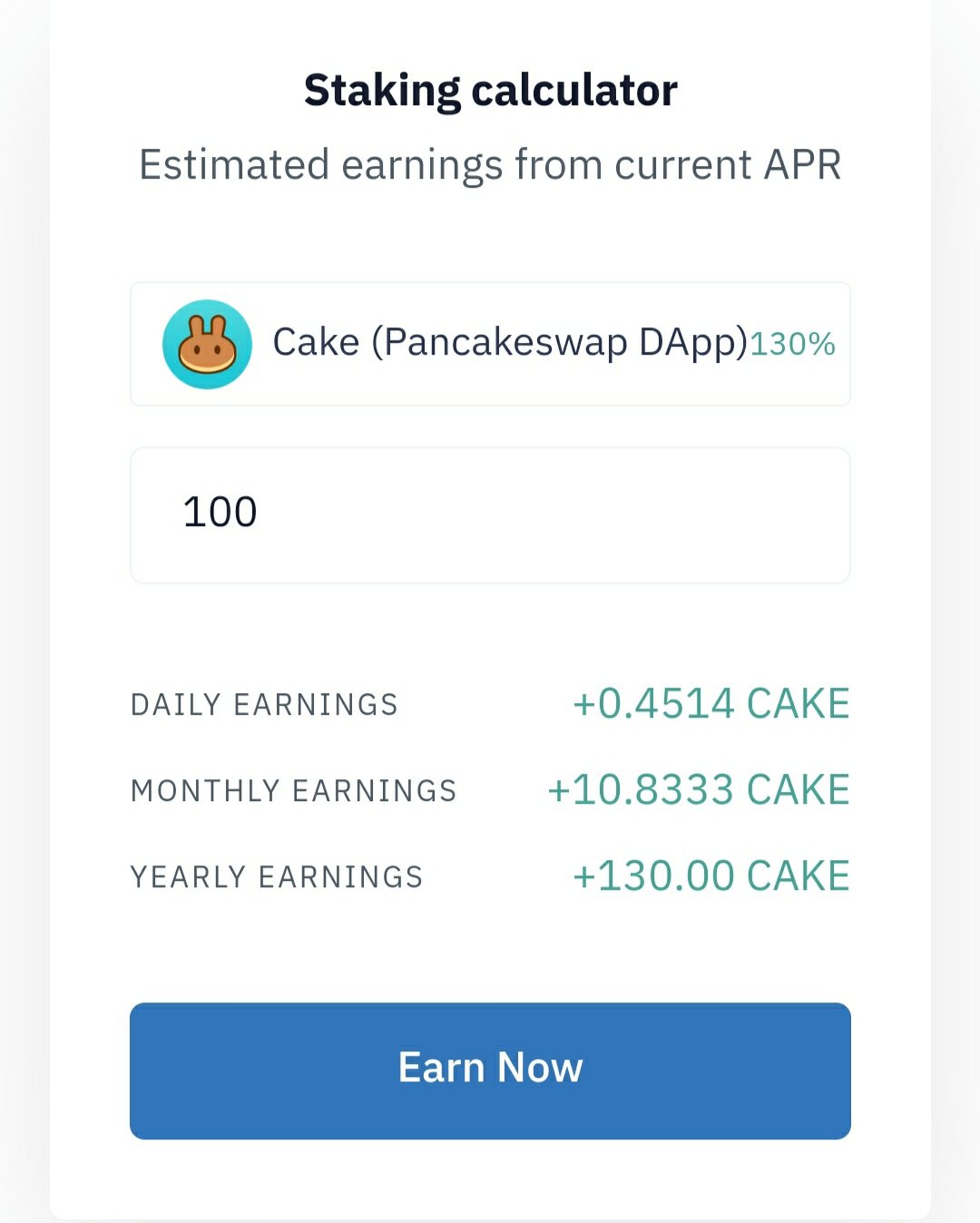
When a user decides to stake tokens in a PoS blockchain, they will need to have a balance in their wallet. The balance should meet that network’s minimum requirement. The node will stake that currency by depositing it into the network. This works similarly to a traditional security deposit.
How much has been staked is directly proportional to the likelihood that your node will be able to cast the next block. Therefore, the more a user stakes on the network, the potential there is for higher staking reward rates.
Just as a miner would get a reward on a proof-of-work chain, when a node successfully completes a block, the user who has helped validate that transaction receives a reward.
Like many other passive income methods, staking has some downsides are risks. Staking is an activity that’s unique to crypto assets. One risk to keep in mind is possible attempts to double-sign or attack the network. If such attacks happen, they will result in the user losing part of their stake. Another downside of staking is the lockup periods. If you want easy access to your funds and assets at all times, lockup periods are something to be aware of.
WHERE CAN I STAKE CRYPTO?
Coins can be staked through cryptocurrency wallets, be it through major exchanges like Binance, or Coinbase, or in the form of ‘cold staking’ on offline and private wallets. If cold staking, a user must keep their staked coins in the same address as moving them can break up the lock-up period. This can have the unintended consequence of a user losing their earned staking rewards. Notable cold storage wallets include Ledger, Trust Wallet, and Atomic wallet, among others.
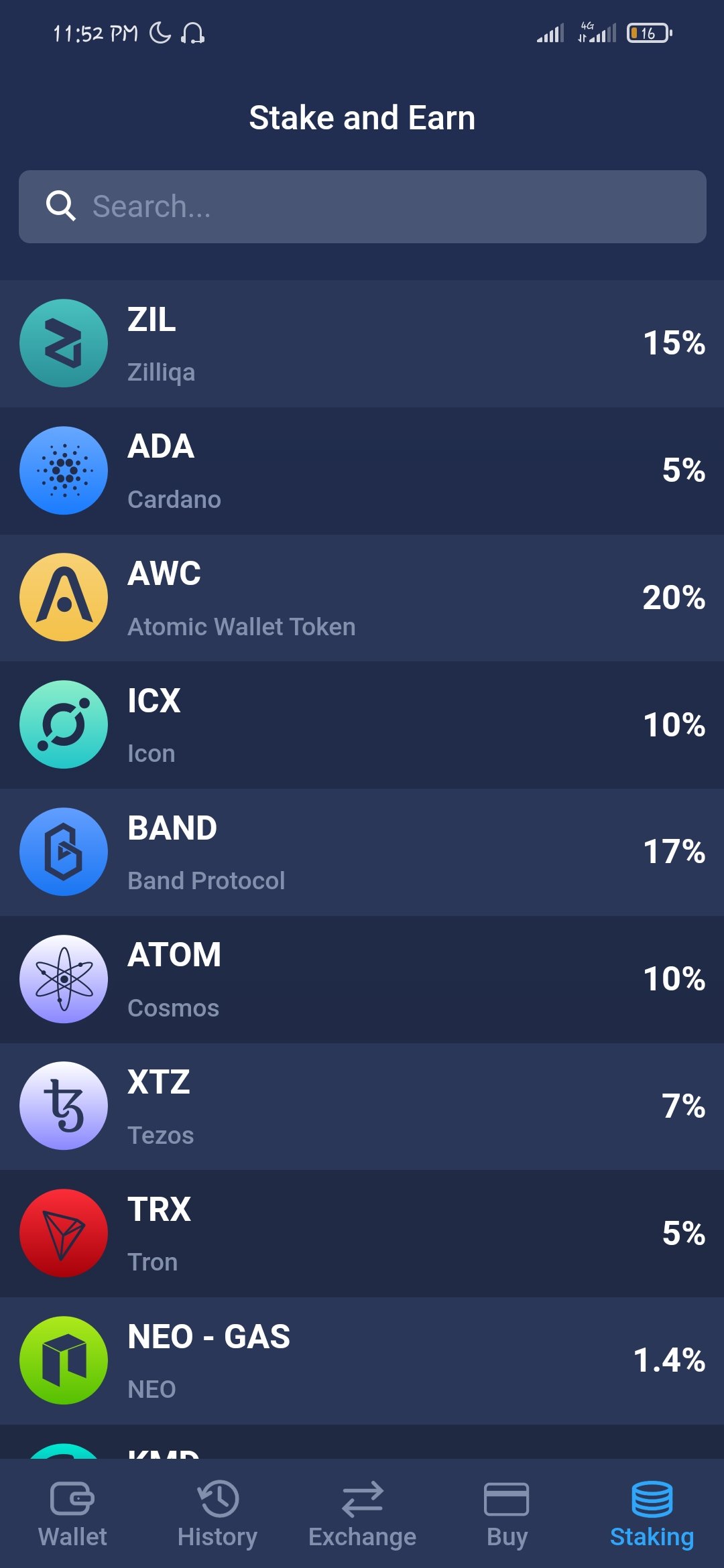
Coins can also be staked on what are known as Staking-as-a-Service Platforms. It is important that users familiarize themselves with the risks and rewards associated with these financial services. Above all, users should understand that these services will take a percentage of the earned rewards for services rendered.
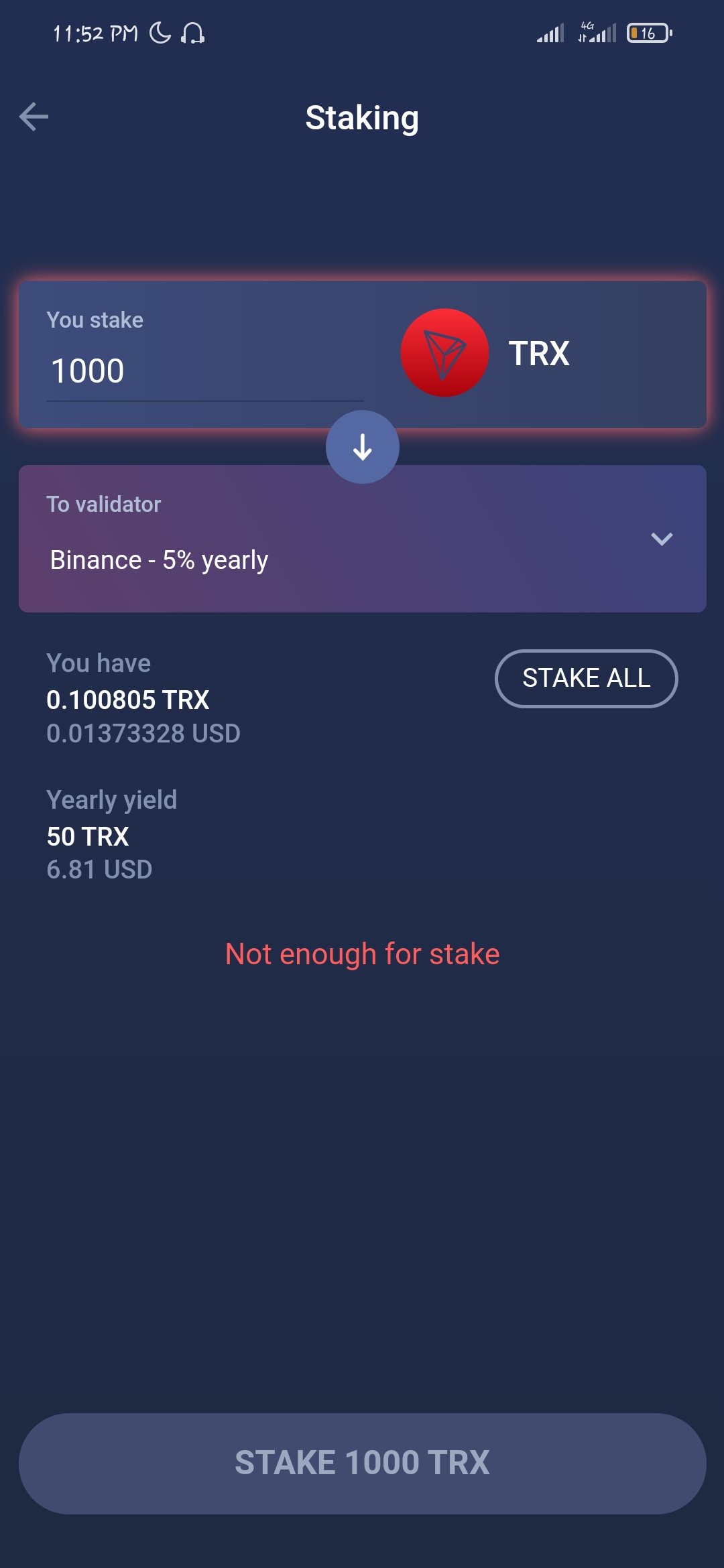
HOW CAN I START STAKING CRYPTO LETS USE THE EXAMPLE OF TRONS ON ATOMIC WALLET.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
Crypto enthusiasts argue which consensus mechanism is fairer. Is proof of stake better than proof of work? Some analysts argue that PoS is less secure than PoW. At the same time, PoS networks can scale times faster than PoW. Henry Brade, Executive Vice President at Coinmotion, Bitcoin & crypto speaker and enthusiast, explains the differences between the mechanisms.
“I think that the whole thing is a tradeoff. It seems that the more subjective (PoS) blockchains are much better and suit Decentral Finance purposes for technical scaling. Ethereum and Cardano are good examples of that. Of course, XRP is the network closest to fiat systems in terms of subjectivity.
However, for the purpose of truly decentralized, censorship-resistant, secure storing and transfer of value, and the role of digital gold, Bitcoin (based on PoW) is unbeatable. But it is a different use case.
In the long run, there will come a time when we will truly see the difference between PoS and PoW. It might take decades. But at some point, these PoS chains may be controlled over 50% by only a couple of wealthy entities. Those entities could be pressured to make changes to the rules of the system and the status of particular transactions. Meanwhile, Bitcoin will likely be immune to this. Then we will see the actual difference between these systems. But for now, it is hard to see.”